Directory is basically a structure that contains all the corresponding documents, files, and folders.
Python’s os module contains multiple functions for directory management.
Python directories functions
| os.access(path, mode) It uses the uid to check for the path’s access. |
| os.chdir(path) It changes the CWD to the path specified by the user. |
| os.chflags(path, flags) It is used to set the flags to the numeric flags. |
| os.chmod(path, mode) It is used to change the path’s mode to the numeric mode. |
| os.chown(path, uid, gid) It changes the group id and owner of path to the numeric uid and gid. |
| os.chroot(path) It is used to change the root directory of the currently executing process to the path specified by the user. |
| os.fchdir(fd) It is used to change the CWD to the directory represented in the file descriptor fd. |
| os.getcwd() It returns the current working directory (CWD). |
| os.getcwdu() It returns Unicode object as output, represented by the CWD. |
| os.lchmod(path, mode) It is used to change the path’s mode to the numeric mode. |
| os.listdir(path) Returns a list containing the names of the entries in the directory given by path. |
| os.lstat(path) |
| os.makedirs(path[, mode]) It is used to create the directories in a recursive manner. |
| os.mkdir( ) It is used to creates a new directory with a named path. |
| os.mkfifo(path[, mode]) |
| os.readlink(path) |
| os.removedirs(path) It is used to remove the corresponding directories recursively. |
| os.rename(src, dst) It is used to rename the src directory to the dst. |
| os.renames(old, new) It is used to rename the old directories with a new one in a recursive manner. |
| os.rmdir(path) It is used to remove the directory specified by the user. |
| os.stat(path) |
1. Creating of a New Directory
Python’s os module provides mkdir() function to create a new directory.
Syntax:
os.mkdir('name')import os
os.mkdir('C:/python1') #create a direcotry abc in C:
Output:
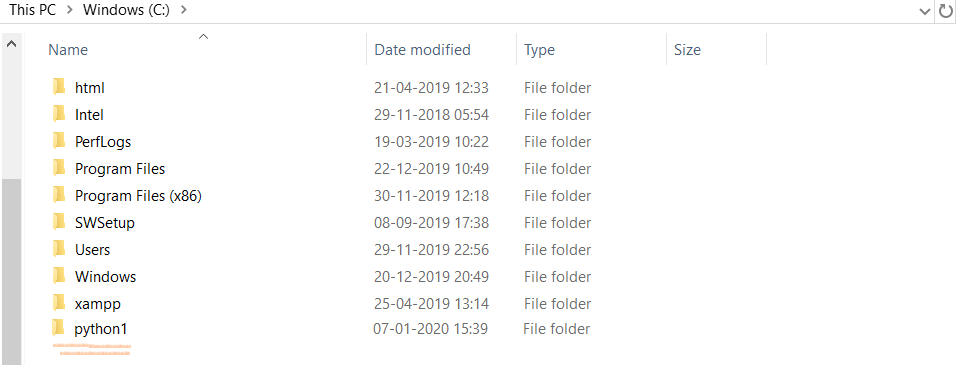
2. Get the Current Working Directory
The getcwd() function is used to get the location of the CWD.
import os
os.getcwd()
Output:
wdir='C:/Users/HP/PycharmProjects/Hello'3. Rename a Directory
The rename() function is used to rename the CWD.
Syntax:
os.rename(old,new)4. Fetch the List of Files/Directories in a Directory
The listdir() function is used to get the list of all the directories and files present in the current directory.
import os
os.listdir('C:\\Users\\HP')
Output:
['.android', '.AndroidStudio3.5', '.crashlytics', '.eclipse', '.emulator_console_auth_token', '.gradle', '.idlerc', '.m2', '.nbi', '.netbeans-derby', '.p2', '.PyCharm2019.3', '.RapidMiner', '.tooling', '.vscode', '3D Objects', 'Anaconda3', 'Anaconda3_1', 'AndroidStudioProjects', 'AppData', 'Application Data', 'Contacts', 'Cookies', 'Desktop', 'Documents', 'Downloads', 'eclipse', 'eclipse-workspace', 'Favorites', 'get-pip.py', 'HP', 'IntelGraphicsProfiles', 'Links', 'Local Settings', 'MicrosoftEdgeBackups']5. Remove a Directory in Python
The rmdir() function is used to delete a directory, which is already empty. If the directory is not empty, it won’t be deleted.
import os
os.rmdir('C:\\Users\\HP\\Pictures\\Screenshots\\python')
6. Check if a Python directory exists
The os.path.exists(path) function is used to check whether a particular directory exists or not.
import os
os.path.exists('C:\\Users\\HP\\Pictures\\Screenshots')
Output:
TrueConclusion
Python os module provides multiple functions to work with directories. We learned how to create, rename, and delete directories in a Python program.
References
- Python Directory Operations
- Directory Documentation

